Understanding the Endocrine System : Functions, Key Glands and Health Tips
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones, which are vital for regulating various bodily functions. These hormones control processes such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood. In this blog post, we’ll explore the anatomy and functions of the endocrine system, common endocrine disorders, and tips for maintaining endocrine health.
Functions of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. Its primary functions include:
1. Hormone Production
Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones act as chemical messengers, influencing various physiological activities.
2. Metabolism Regulation
Hormones help regulate metabolism, which includes the processes of energy production, storage, and utilization.
3. Growth and Development
Hormones are essential for normal growth and development, especially during childhood and adolescence.
4. Reproduction
The endocrine system regulates reproductive processes, including sexual development, menstrual cycles, and pregnancy.
5. Response to Stress
Hormones help the body respond to stress by preparing it for a “fight or flight” reaction.
6. Homeostasis
The endocrine system helps maintain internal balance by regulating blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and other critical parameters.
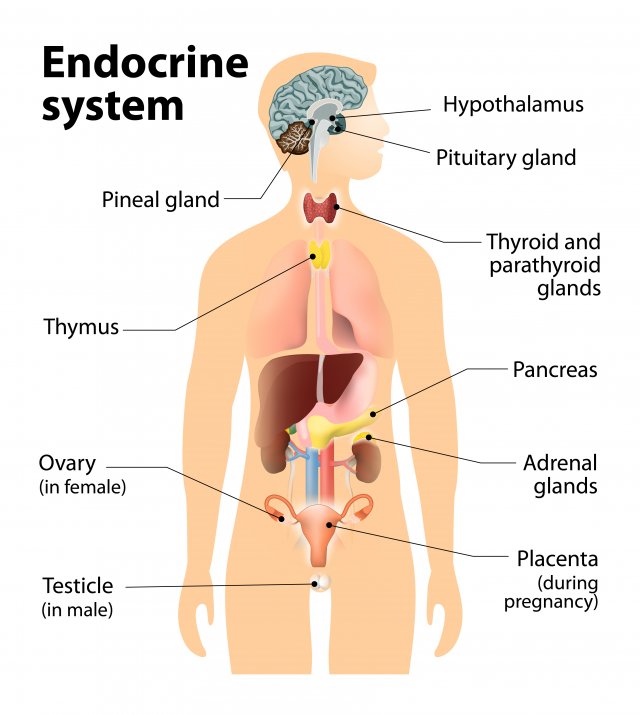
Key Glands of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system consists of several glands, each responsible for producing specific hormones:
1. Hypothalamus
- Location: Brain
- Functions: Links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. Regulates hunger, thirst, sleep, and body temperature.
2. Pituitary Gland
- Location: Base of the brain
- Functions: Known as the “master gland,” it controls other endocrine glands and regulates growth, metabolism, and reproductive processes.
3. Thyroid Gland
- Location: Neck
- Functions: Regulates metabolism, energy production, and growth through the production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4).
4. Parathyroid Glands
- Location: Behind the thyroid gland
- Functions: Regulate calcium levels in the blood and bone metabolism through parathyroid hormone (PTH).
5. Adrenal Glands
- Location: On top of the kidneys
- Functions: Produce hormones like cortisol and adrenaline that help regulate metabolism, immune response, and stress.
6. Pancreas
- Location: Abdomen
- Functions: Produces insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels.
7. Gonads (Ovaries and Testes)
- Location: Pelvic area (ovaries in females, testes in males)
- Functions: Produce sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone) that regulate reproductive functions and secondary sexual characteristics.
8. Pineal Gland
- Location: Brain
- Functions: Produces melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles.
Common Endocrine Disorders
1. Diabetes Mellitus
A condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insufficient insulin production (Type 1) or insulin resistance (Type 2).
2. Hypothyroidism
A condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, leading to fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
3. Hyperthyroidism
A condition where the thyroid gland produces excessive thyroid hormones, causing symptoms like weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and nervousness.
4. Addison’s Disease
A disorder where the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol, leading to fatigue, low blood pressure, and weight loss.
5. Cushing’s Syndrome
A condition caused by excessive cortisol production, leading to weight gain, high blood pressure, and a rounded face.
6. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
A hormonal disorder in females characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excess hair growth, and ovarian cysts.
Tips for Maintaining Endocrine Health
1. Maintain a Balanced Diet
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Avoid excessive sugar and refined carbohydrates to help regulate blood sugar levels.
2. Exercise Regularly
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to help regulate hormones and improve metabolic health.
3. Get Adequate Sleep
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support hormonal balance and overall health.
4. Manage Stress
- Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises.
5. Avoid Endocrine Disruptors
- Limit exposure to chemicals that can interfere with hormone function, such as BPA (found in plastics), phthalates, and certain pesticides.
6. Regular Check-ups
- Visit your healthcare provider for regular check-ups and screenings to detect and manage endocrine disorders early.
7. Stay Hydrated
- Drink plenty of water to support overall health and the proper functioning of endocrine glands.
Conclusion
The endocrine system is vital for regulating many of the body’s processes, from metabolism and growth to stress response and reproduction. Understanding its key functions and maintaining endocrine health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management can help ensure overall well-being. Regular medical check-ups are also essential to detect and manage any endocrine disorders promptly.






