Comprehensive Care for a Client with Lower Gastrointestinal Tract Health Problems: An NCLEX-Standard Guide
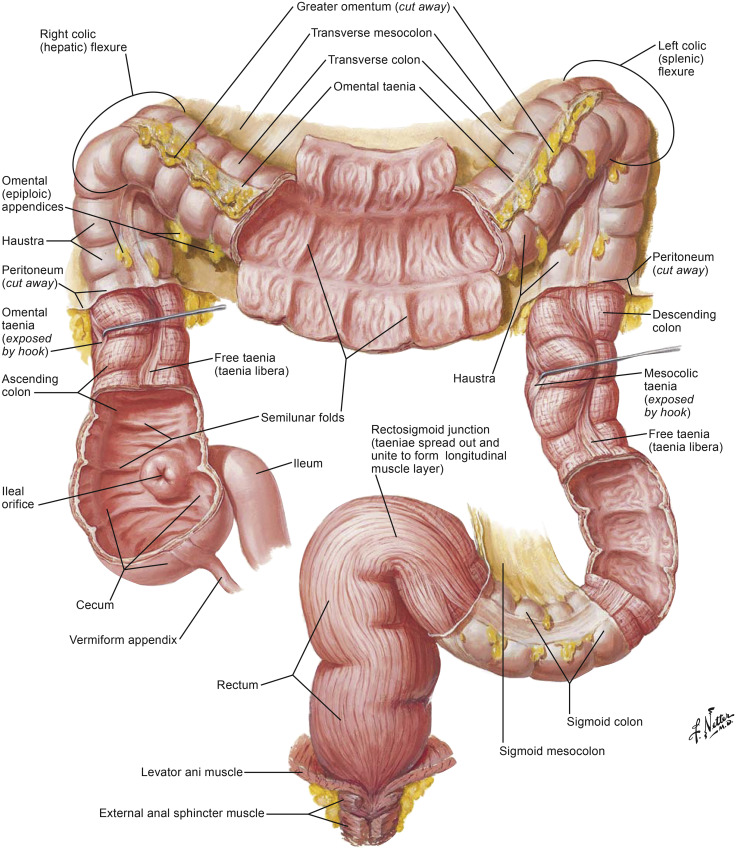
Client with Lower Gastrointestinal Tract Health Proble
Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract health problems encompass a range of conditions affecting the small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. These issues can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life and overall health. This guide adheres to NCLEX standards and covers essential aspects of managing a client with lower GI tract problems, including assessment, common conditions, treatment options, nursing interventions, and patient education.
Understanding Lower Gastrointestinal Tract Problems
The lower GI tract includes the small intestine (jejunum and ileum), large intestine (colon), rectum, and anus. Common health problems in this area include inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diverticulitis, colorectal cancer, and hemorrhoids.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of lower GI tract problems can vary but often include:
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Bloating and gas
- Rectal bleeding
- Changes in stool consistency or frequency
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
Common Conditions
1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Types:
- Crohn’s Disease: Can affect any part of the GI tract, commonly the terminal ileum and colon.
- Ulcerative Colitis: Limited to the colon and rectum.
Symptoms:
- Persistent diarrhea
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Rectal bleeding
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
Treatment:
- Medications (aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, biologics)
- Nutritional support
- Surgery (resection or colectomy) in severe cases
2. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Symptoms:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Bloating and gas
- Diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between both
- Mucus in stool
Treatment:
- Dietary modifications (low FODMAP diet, fiber supplements)
- Medications (antispasmodics, laxatives, antidiarrheals)
- Stress management techniques
3. Diverticulitis
Symptoms:
- Lower left abdominal pain
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Changes in bowel habits
Treatment:
- Antibiotics for infection
- Clear liquid diet progressing to low-fiber diet during acute episodes
- Surgery for complications (abscess, perforation)
4. Colorectal Cancer
Symptoms:
- Changes in bowel habits
- Rectal bleeding or blood in stool
- Abdominal discomfort
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
Treatment:
- Surgery (resection, colectomy)
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy
5. Hemorrhoids
Symptoms:
- Rectal bleeding
- Itching or irritation
- Pain or discomfort
- Swelling around the anus
Treatment:
- Dietary changes (high-fiber diet)
- Medications (topical treatments, stool softeners)
- Procedures (rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, hemorrhoidectomy)
Nursing Care and Considerations
1. Comprehensive Assessment
- History Taking: Obtain a detailed medical history, including previous GI issues, medication use, lifestyle factors, and family history.
- Physical Examination: Perform a thorough physical exam, focusing on the abdomen and rectum.
- Diagnostic Tests: Ensure completion of necessary tests such as colonoscopy, CT scan, stool tests, and blood tests.
2. Symptom Management
- Pain Control: Regularly assess pain levels and administer prescribed pain relief medications.
- Bowel Management: Monitor bowel habits, provide dietary recommendations, and administer medications as needed.
- Hydration: Ensure adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration.
3. Patient Education
- Dietary Changes: Educate on the importance of a diet that supports GI health (e.g., high-fiber diet for constipation, low-FODMAP diet for IBS).
- Medication Adherence: Emphasize the importance of taking prescribed medications as directed and understanding potential side effects.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Encourage regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding triggers that exacerbate symptoms.
4. Psychological Support
- Emotional Support: Provide a supportive environment and address any anxieties or fears the client may have.
- Counseling: Refer to counseling services if needed to help cope with chronic illness.
- Support Groups: Encourage participation in support groups for emotional and psychological support.
5. Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor vital signs, lab results, and symptoms regularly to detect any changes in condition.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Ensure the client attends follow-up appointments for ongoing assessment and treatment adjustments.
Case Study: Managing a Client with Crohn’s Disease
Background
Mr. Lee, a 28-year-old male, presents with persistent diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. He has been diagnosed with Crohn’s disease affecting the terminal ileum.
Assessment
- History: Detailed history of symptoms, exacerbations, medication use, and lifestyle factors.
- Physical Exam: Abdominal tenderness and palpable mass in the right lower quadrant.
- Diagnostic Tests: Colonoscopy reveals inflamed and ulcerated areas in the terminal ileum; blood tests show anemia and elevated inflammatory markers.
Treatment Plan
- Medications:
- Aminosalicylates to reduce inflammation
- Corticosteroids for acute exacerbations
- Immunomodulators and biologics for long-term management
- Nutritional Support:
- High-calorie, nutrient-dense diet
- Small, frequent meals
- Vitamin and mineral supplements
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Stress management techniques
- Regular exercise tailored to ability
- Smoking cessation
- Surgery:
- Resection of the affected area if medically indicated
Nursing Interventions
- Education: Provided detailed instructions on medication regimen, dietary changes, and management of symptoms.
- Symptom Management: Administered prescribed medications and monitored for side effects.
- Support: Provided emotional support and referred to counseling services as needed.
Nursing Considerations
1. Pain Management
- Assessment: Regularly assess pain using standardized pain scales and adjust pain management strategies as needed.
- Interventions: Administer prescribed pain medications and provide non-pharmacological pain relief methods.
2. Infection Prevention
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: Monitor for signs of infection and educate the client on preventive measures.
- Hand Hygiene: Emphasize the importance of proper hand hygiene.
3. Nutrition and Hydration
- Dietary Support: Provide dietary recommendations to support overall health and manage symptoms.
- Hydration: Encourage adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration.






