Mastering Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack) in Preparation for NCLEX Exam
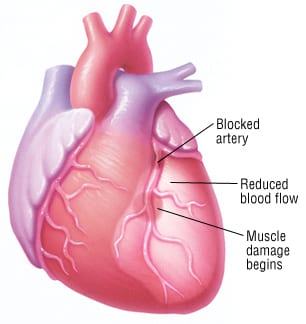
Myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, is a critical topic for the NCLEX exam. Understanding the pathophysiology, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of MI is essential for providing effective nursing care. This blog post provides a comprehensive guide to help you prepare for the NCLEX exam.
What is Myocardial Infarction?
Myocardial infarction occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked for a prolonged period, leading to damage or death of the heart muscle tissue. This blockage is usually caused by a buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries, which can rupture and form a clot, obstructing blood flow.
Pathophysiology
MI typically results from the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque in a coronary artery, followed by the formation of a thrombus (blood clot) that occludes the artery. This leads to ischemia (lack of oxygen) and subsequent necrosis (death) of the heart muscle supplied by that artery.
Symptoms
- Chest Pain: Intense, crushing, or squeezing pain in the center or left side of the chest, often radiating to the neck, jaw, shoulder, back, or arm.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially with exertion.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Often accompanying chest pain.
- Sweating: Profuse sweating, often described as cold sweat.
- Fatigue: Unusual fatigue, especially in women.
- Lightheadedness or Dizziness: Feeling faint or dizzy.
- Anxiety: A feeling of impending doom.
Risk Factors
- Smoking
- High Blood Pressure
- High Cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical Inactivity
- Family History of Heart Disease
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Gender (males are at higher risk)
Diagnosis
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG): Detects changes in the heart’s electrical activity indicative of MI.
- Blood Tests: Measure cardiac enzymes such as troponin and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), which are released into the blood when heart muscle is damaged.
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to visualize the heart and assess damage.
- Coronary Angiography: Involves injecting a contrast dye into the coronary arteries to visualize blockages using X-ray imaging.
Management
Acute Management
- MONA Protocol: Includes Morphine, Oxygen, Nitroglycerin, and Aspirin.
- Antiplatelet Agents: Such as aspirin and clopidogrel to prevent further clotting.
- Anticoagulants: Like heparin to reduce clot formation.
- Beta-Blockers: To decrease heart rate and myocardial oxygen demand.
- Thrombolytic Therapy: Administered to dissolve clots if PCI is not available.
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): Also known as angioplasty, involves inserting a stent to open the blocked artery.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): Surgery to bypass blocked coronary arteries using grafts.
Long-term Management
- Medications: Including ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, statins, and antiplatelet agents.
- Lifestyle Changes: Such as smoking cessation, a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: A supervised program to improve cardiovascular health through exercise and education.
- Regular Monitoring: Follow-up appointments to monitor heart health and manage risk factors.
Complications
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms that can be life-threatening.
- Heart Failure: Inability of the heart to pump blood effectively.
- Cardiogenic Shock: Severe form of heart failure with inadequate blood flow to the organs.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart.
- Ventricular Aneurysm: Bulging of the weakened area of the heart wall.
NCLEX Preparation Tips for Myocardial Infarction
- Understand Pathophysiology: Be clear about how MI occurs and the underlying mechanisms.
- Memorize Key Symptoms: Recognize the classic and atypical symptoms of MI.
- Diagnostic Tools: Familiarize yourself with the various tests used to diagnose MI and their significance.
- Management Strategies: Know the acute and long-term management protocols for MI.
- Complications: Be aware of potential complications following an MI and their interventions.
- Practice Questions: Utilize NCLEX practice questions focused on MI to reinforce your knowledge and improve your test-taking skills.






