Navigating Biliary Tract Disorders: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Managing
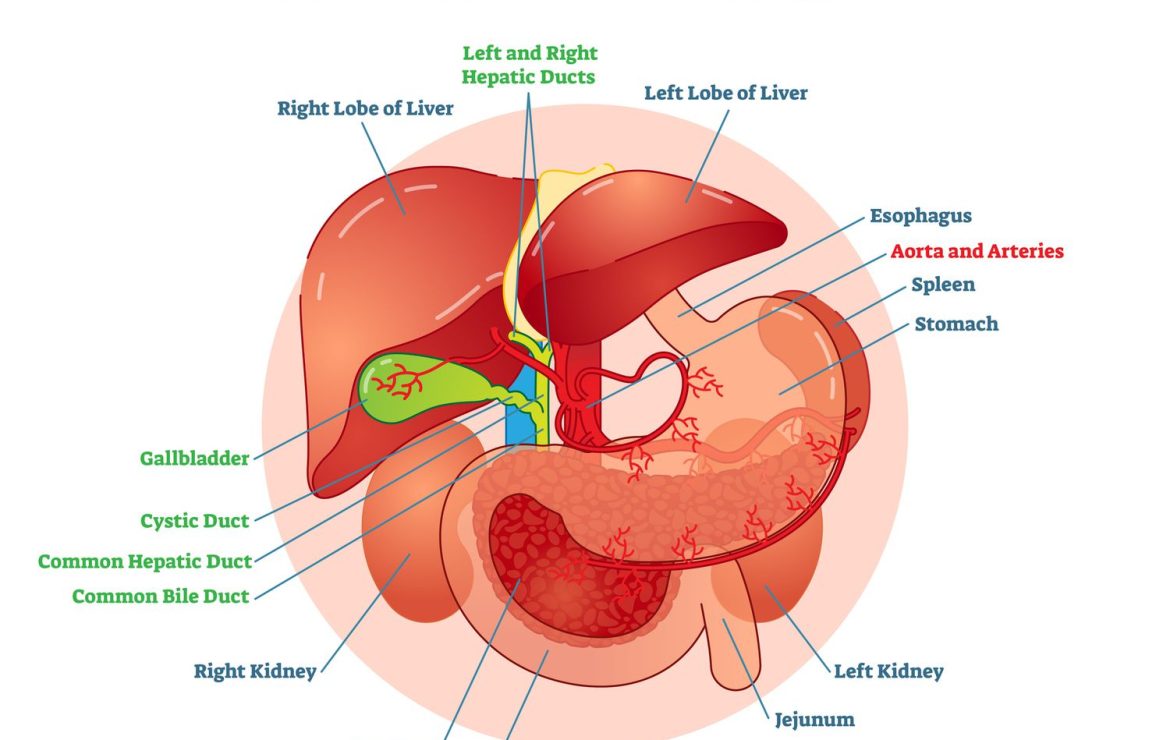
Biliary tract disorders encompass a range of conditions that affect the bile ducts, gallbladder, and related structures. These disorders can significantly impact a client’s health and quality of life, leading to symptoms such as pain, jaundice, and digestive issues. In this blog post, we will explore the common types of biliary tract disorders, their symptoms, diagnostic methods, and effective nursing management strategies.
Understanding Biliary Tract Disorders
The biliary tract includes the bile ducts, gallbladder, and associated structures involved in the production, storage, and transportation of bile. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats. Common biliary tract disorders include cholelithiasis (gallstones), cholecystitis, choledocholithiasis, and cholangitis.
1. Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
- Description: Formation of stones within the gallbladder due to the precipitation of bile components.
- Types: Cholesterol stones and pigment stones.
- Symptoms: Often asymptomatic; however, when symptoms occur, they include right upper quadrant pain, nausea, vomiting, and possible jaundice.
2. Cholecystitis
- Description: Inflammation of the gallbladder, usually due to gallstones obstructing the cystic duct.
- Symptoms: Severe right upper quadrant pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, and tenderness over the gallbladder (Murphy’s sign).
3. Choledocholithiasis
- Description: Presence of gallstones in the common bile duct.
- Symptoms: Similar to cholelithiasis but may also include jaundice, dark urine, light-colored stools, and intense pain.
4. Cholangitis
- Description: Inflammation and infection of the bile ducts, often caused by bacterial infection due to bile duct obstruction.
- Symptoms: Charcot’s triad (fever, jaundice, and right upper quadrant pain), and in severe cases, Reynold’s pentad (Charcot’s triad plus hypotension and mental confusion).
Diagnosis of Biliary Tract Disorders
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management. Diagnostic methods include:
1. Physical Examination
- Assess for signs such as jaundice, abdominal tenderness, and Murphy’s sign.
2. Laboratory Tests
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs): Elevated levels of bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and aminotransferases (AST and ALT) may indicate biliary obstruction or inflammation.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Elevated white blood cell count may indicate infection.
3. Imaging Studies
- Ultrasound: First-line imaging for detecting gallstones and assessing the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the biliary and surrounding structures.
- MRI/MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography): Non-invasive imaging to visualize the bile ducts.
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): Combines endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat bile duct conditions.
Nursing Management of Biliary Tract Disorders
Effective nursing management involves a combination of monitoring, patient education, pain management, and preparation for potential surgical interventions.
1. Pain Management
- Medications: Administer prescribed analgesics, such as NSAIDs or opioids, to manage pain.
- Non-Pharmacological Interventions: Encourage relaxation techniques, positioning for comfort, and application of heat to alleviate pain.
2. Monitoring and Assessment
- Vital Signs: Regularly monitor for signs of infection (fever, tachycardia) and complications (hypotension, changes in mental status).
- Abdominal Assessment: Monitor for changes in pain, abdominal distension, and tenderness.
- Lab Results: Keep track of liver function tests and CBC to assess for worsening of the condition or complications.
3. Patient Education
- Dietary Modifications: Educate clients to avoid fatty foods that can exacerbate symptoms. Recommend a low-fat diet.
- Symptom Management: Teach clients to recognize symptoms of complications, such as severe pain, jaundice, or signs of infection, and to seek medical attention promptly.
- Postoperative Care: For clients undergoing cholecystectomy, provide instructions on wound care, activity restrictions, and signs of infection to watch for.
4. Surgical Interventions
- Cholecystectomy: Surgical removal of the gallbladder, often performed laparoscopically. Provide preoperative and postoperative care, including monitoring for complications and educating clients on recovery.
- ERCP: Used to remove stones from the bile ducts. Prepare clients for the procedure and provide post-procedure care, including monitoring for signs of pancreatitis or perforation.
Case Study and NCLEX-Style Questions
Case Study:
A 45-year-old female presents with severe right upper quadrant pain, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice. Ultrasound confirms the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct (choledocholithiasis). Her LFTs show elevated bilirubin and ALP levels.
NCLEX-Style Questions:
Question 1: Which of the following is the priority nursing intervention for this client?
- A. Administering prescribed pain medication.
- B. Preparing the client for ERCP.
- C. Educating the client on dietary modifications.
- D. Monitoring the client’s urine output.
Answer: B. Preparing the client for ERCP is the priority intervention as it will directly address the cause of her symptoms by removing the obstructing gallstones.
Question 2: What is a key sign that the nurse should monitor for to detect possible cholangitis in this client?
- A. Increased appetite
- B. Charcot’s triad (fever, jaundice, right upper quadrant pain)
- C. Elevated blood glucose levels
- D. Hypoactive bowel sounds
Answer: B. Charcot’s triad is indicative of cholangitis and should be closely monitored in this client.
Conclusion
Managing biliary tract disorders requires a comprehensive approach that includes accurate diagnosis, effective pain management, vigilant monitoring, and thorough patient education. As a nursing professional preparing for the NCLEX, mastering these concepts will enhance your ability to provide quality care for clients with biliary tract disorders. Remember to stay informed about the latest best practices and interventions to ensure positive outcomes for your patients.






