RENAL AND URINARY DISORDERS: MANAGING UTIs, KIDNEY STONES, AND DIALYSIS CARE.
Introduction:
Renal and urinary disorders are common but can be complex, affecting individuals across all ages and requiring specialized management. Urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, and dialysis care are three critical areas within this category, each requiring specific care approaches to ensure effective management and improve patient outcomes. This post will cover practical, evidence-based nursing care strategies for UTIs, kidney stones, and dialysis patients, focusing on promoting comfort, ensuring patient safety, and educating for long-term health.
1. Managing Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are among the most prevalent bacterial infections, particularly affecting women, older adults, and individuals with compromised immunity. Proper management of UTIs can prevent complications such as kidney infections and recurrent UTIs.
• Symptoms of UTIs: Common symptoms include frequent and painful urination, urgency, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and lower abdominal pain. Older adults may exhibit atypical symptoms, such as confusion or changes in behavior.
• Treatment Approach: Antibiotic therapy is the primary treatment for UTIs. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics to avoid resistance. Nurses should also educate patients on the importance of hydration to help flush out bacteria.
• Preventative Measures: Encourage patients to maintain good hydration, practice good personal hygiene, and avoid irritants such as perfumed soaps. For recurrent UTIs, cranberry supplements may be suggested, though evidence on effectiveness is mixed.
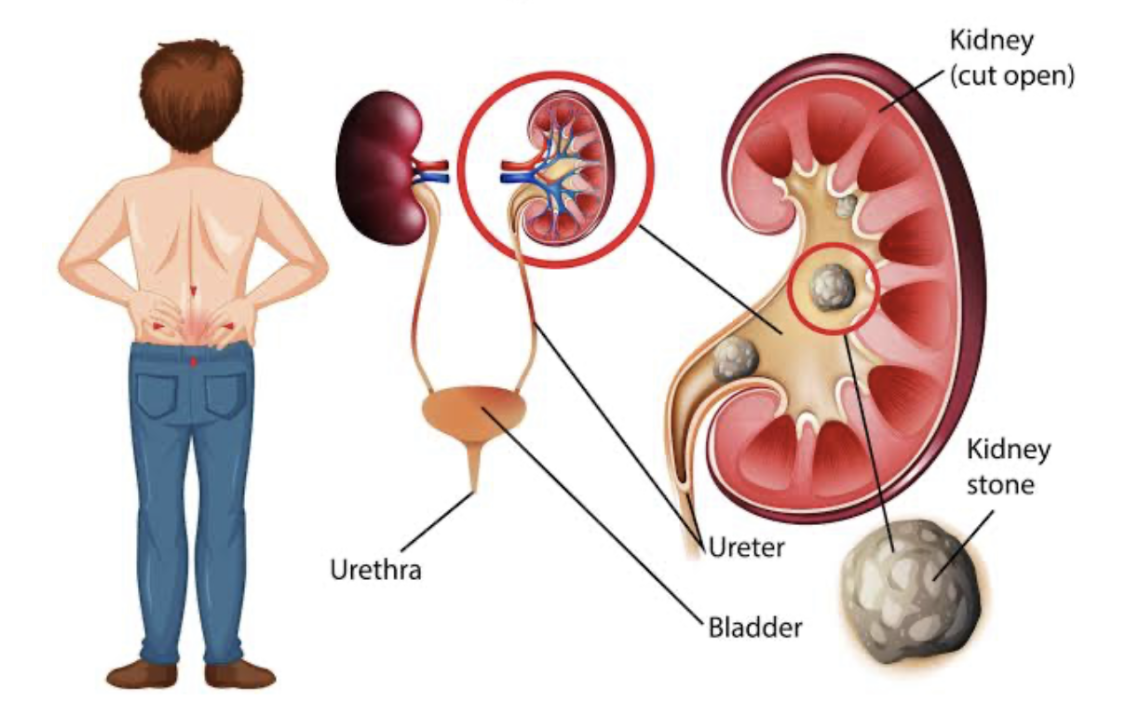
2. Managing Kidney Stones
Kidney stones, or renal calculi, can cause severe pain and lead to complications if not managed correctly. Treatment varies depending on the stone’s size, location, and the patient’s overall health.
• Symptoms of Kidney Stones: Severe, sharp pain in the side or back, pain radiating to the lower abdomen and groin, nausea, and hematuria (blood in urine) are common indicators.
• Pain Management: Pain is the most intense symptom, and appropriate pain control is a nursing priority. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often effective, but opioids may be needed in severe cases.
• Fluid Management and Stone Expulsion: Encourage patients to increase fluid intake to promote stone expulsion. Some patients may require medications to facilitate stone passage or alter urine acidity. For larger stones, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) may be necessary.
• Dietary Modifications: Patients should avoid oxalate-rich foods (e.g., spinach, nuts) and limit sodium intake to reduce recurrence risk. Dietary recommendations may vary based on the stone composition (e.g., calcium oxalate, uric acid).
3. Dialysis Care
Dialysis is a lifesaving treatment for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) when kidney function is no longer sufficient to meet the body’s needs. There are two primary forms of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
• Hemodialysis: This involves filtering the blood through a machine outside the body. Nurses play a crucial role in maintaining vascular access, monitoring for complications like hypotension, infection, or access site issues.
• Patient Education: Patients should understand the importance of adhering to dialysis schedules and dietary restrictions. High-potassium foods and excessive fluid intake are restricted to prevent complications.
• Peritoneal Dialysis: This process uses the lining of the abdominal cavity to filter waste. Nursing care focuses on maintaining catheter site hygiene, monitoring for signs of peritonitis, and providing patient education on aseptic technique.
• Dietary and Fluid Management: Unlike hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis patients often have more flexible dietary restrictions, although they may still need to limit phosphorus and potassium intake.
NCLEX-Style Questions and Answers
1. Question: A patient with a UTI is being discharged with a prescription for antibiotics. What is the most important information for the nurse to provide?
• A: Take antibiotics only if symptoms worsen.
• B: Stop the antibiotic once symptoms resolve.
• C: Complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed.
• D: Increase caffeine intake to help flush out bacteria.
Answer: C. Completing the entire course of antibiotics is essential to prevent recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
2. Question: A nurse is caring for a patient with kidney stones experiencing severe flank pain. Which of the following is the nurse’s priority action?
• A: Encourage the patient to ambulate.
• B: Administer prescribed pain medication.
• C: Provide warm compresses to the abdomen.
• D: Encourage increased fluid intake.
Answer: B. Pain management is a priority to provide relief and allow the patient to rest comfortably.
3. Question: A nurse is educating a patient on peritoneal dialysis about signs of peritonitis. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
• A: “I should report cloudy drainage immediately.”
• B: “If I have abdominal pain, I should call my healthcare provider.”
• C: “It’s normal for the dialysis fluid to have a foul odor.”
• D: “Fever is a sign of infection that I should report.”
Answer: C. A foul odor in dialysis fluid may indicate infection, which is not normal and requires prompt medical attention.
Conclusion:
Renal and urinary disorders such as UTIs, kidney stones, and ESRD demand careful management to minimize complications and improve patients’ quality of life. Understanding symptoms, treatment options, and preventative strategies can empower patients and caregivers to manage these conditions effectively. Nurses play a pivotal role in educating patients, promoting adherence to care plans, and ensuring safety in all aspects of renal and urinary disorder management. With the right approach, patients can lead healthier, more comfortable lives while navigating these challenges






