Understanding Urinary Tract Health: A Comprehensive Guide
Urinary tract health is an essential aspect of overall well-being, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Problems in the urinary tract can cause significant discomfort and potentially lead to severe health issues if not addressed promptly. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of urinary tract health, common problems, symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures.
What is the Urinary Tract?
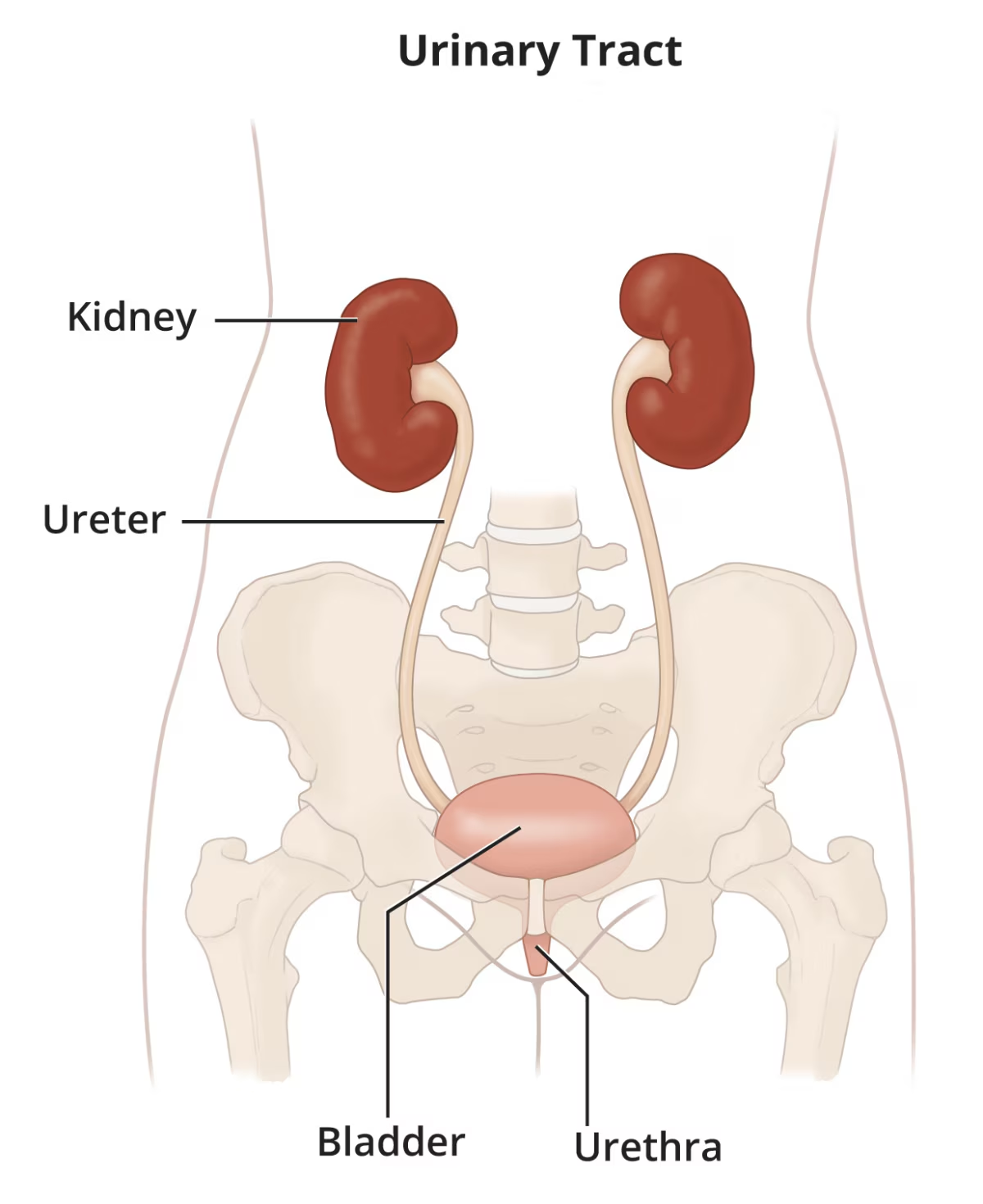
The urinary tract is a system in the body responsible for removing waste and excess fluid in the form of urine. It includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Here’s a brief overview of each component:
- Kidneys: Two bean-shaped organs that filter blood to produce urine.
- Ureters: Tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like organ that stores urine until it is expelled from the body.
- Urethra: The tube through which urine exits the body.
Common Urinary Tract Problems
Several issues can affect the urinary tract, leading to discomfort and health complications. Some of the most common problems include:
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are the most frequent urinary tract problem, primarily caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract. Symptoms often include:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain (in women)
- Fever or chills (in severe cases)
Treatment: UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics. It’s crucial to complete the entire course of medication to prevent recurrence.
2. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys. Symptoms include:
- Severe pain in the side and back
- Pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin
- Painful urination
- Pink, red, or brown urine
- Nausea and vomiting
Treatment: Treatment ranges from drinking water to pass small stones to medical procedures for larger stones.
3. Interstitial Cystitis (IC)
Also known as painful bladder syndrome, IC is a chronic condition causing bladder pressure, bladder pain, and sometimes pelvic pain. Symptoms include:
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Frequent urination
- Pain during intercourse
- Persistent urge to urinate
Treatment: IC treatment is varied and may include medications, physical therapy, bladder training, and lifestyle changes.
4. Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer starts in the cells of the bladder. Symptoms can include:
- Blood in the urine
- Frequent urination
- Painful urination
- Back or pelvic pain
Treatment: Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy.
Maintaining Urinary Tract Health
Preventing urinary tract problems involves several proactive steps:
1. Hydration
Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, helps dilute urine and ensures frequent urination, flushing bacteria from the urinary tract.
2. Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene, such as wiping from front to back and avoiding harsh soaps, helps prevent infections.
3. Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain urinary tract health. Cranberry juice is often recommended for its potential UTI-preventing properties.
4. Regular Check-ups
Routine medical check-ups can help detect early signs of urinary tract issues, allowing for timely intervention.
Case Study: Managing a Client with Urinary Tract Health Problems
Let’s consider a case study to understand better how to manage urinary tract health issues.
Background
Jane, a 45-year-old woman, experiences frequent and painful urination, lower abdominal pain, and occasional blood in her urine. She has a history of recurrent UTIs.
Diagnosis
After a thorough medical examination, including a urine test and imaging, Jane is diagnosed with interstitial cystitis (IC).
Treatment Plan
- Medications: Jane is prescribed medications to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Bladder Training: She undergoes bladder training to increase the intervals between urinating.
- Dietary Changes: Jane adopts a diet avoiding potential irritants like caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods.
- Physical Therapy: She attends physical therapy sessions to alleviate pelvic floor dysfunction.
- Regular Monitoring: Jane’s condition is regularly monitored through follow-up appointments and tests to adjust her treatment plan as needed.
Conclusion
Urinary tract health is vital for overall well-being, and understanding common problems, symptoms, and treatments can help manage and prevent these issues. Maintaining good hydration, hygiene, diet, and regular medical check-ups are key steps in ensuring a healthy urinary tract. If you experience any symptoms related to urinary tract issues, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly to receive appropriate treatment.






