Understanding the Respiratory System: Functions, Anatomy, and Health Tips
The respiratory system is a vital organ system responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis and overall health. In this blog post, we’ll explore the anatomy and functions of the respiratory system, common respiratory conditions, and tips for maintaining respiratory health.
Functions of the Respiratory System
The primary function of the respiratory system is gas exchange – supplying oxygen to the bloodstream and removing carbon dioxide. Here are the key functions of the respiratory system:
1. Gas Exchange
- Oxygen from inhaled air diffuses through the walls of the alveoli and into the bloodstream.
- Carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, diffuses from the bloodstream into the alveoli to be exhaled.
2. Regulation of Blood pH
- The respiratory system helps maintain the acid-base balance of the blood by regulating the levels of carbon dioxide.
3. Protection
- The respiratory system filters out particles and pathogens through mechanisms like mucus production and the action of cilia in the airways.
4. Vocalization
- The respiratory system facilitates vocalization and speech by enabling airflow through the vocal cords.
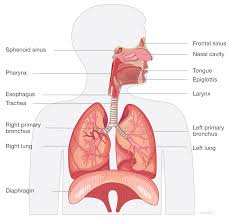
Anatomy of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system consists of the upper and lower respiratory tracts:
1. Upper Respiratory Tract
- Nose and Nasal Cavity: Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air.
- Pharynx (Throat): Passageway for air and food; aids in sound production.
- Larynx (Voice Box): Contains vocal cords and is responsible for sound production.
2. Lower Respiratory Tract
- Trachea (Windpipe): Transports air to the bronchi; lined with cilia to trap particles.
- Bronchi: Two main air passages that branch off the trachea and lead to each lung.
- Bronchioles: Smaller branches of the bronchi that lead to alveoli.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs; surrounded by capillaries.
3. Lungs
- The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system, located in the thoracic cavity.
- They are divided into lobes (three in the right lung, two in the left lung) and are covered by a protective membrane called the pleura.
Common Respiratory Conditions
1. Asthma
- A chronic condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing, wheezing, and coughing.
2. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- A group of diseases, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis, that cause airflow blockage and breathing-related problems.
3. Pneumonia
- An infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus, causing cough, fever, and difficulty breathing.
4. Tuberculosis (TB)
- A bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, affecting the lungs and potentially other parts of the body.
5. Lung Cancer
- A type of cancer that begins in the lungs, often associated with smoking and exposure to carcinogens.
Tips for Maintaining Respiratory Health
1. Avoid Smoking
- Smoking is a major risk factor for many respiratory diseases, including lung cancer, COPD, and emphysema. Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke are crucial for respiratory health.
2. Practice Good Hygiene
- Wash your hands regularly, cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoid close contact with people who are sick to reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
3. Stay Active
- Regular physical activity helps improve lung function and overall respiratory health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
4. Maintain a Healthy Diet
- A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports overall health and can help reduce inflammation in the airways.
5. Get Vaccinated
- Vaccinations, such as the flu vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine, can help prevent respiratory infections and complications.
6. Monitor Air Quality
- Be aware of air quality levels in your area and minimize exposure to pollutants and allergens. Use air purifiers indoors and avoid outdoor activities on days with poor air quality.
7. Practice Breathing Exercises
- Breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing, can help improve lung capacity and efficiency.
Conclusion
The respiratory system is essential for sustaining life by providing oxygen to the body and removing carbon dioxide. Understanding its anatomy and functions helps us appreciate its importance in overall health. By following simple health tips and being mindful of potential respiratory conditions, we can maintain optimal respiratory health and ensure our body’s systems function efficiently.






